Sierra Wireless Device to Cloud platform will provide solution for end to end IoT applications.
The document below is in the following format:
Introduction to Device to Cloud platform
APIs Hackathon
Architecture Explanation
Using the platform
Introduction to Device to Cloud platform->
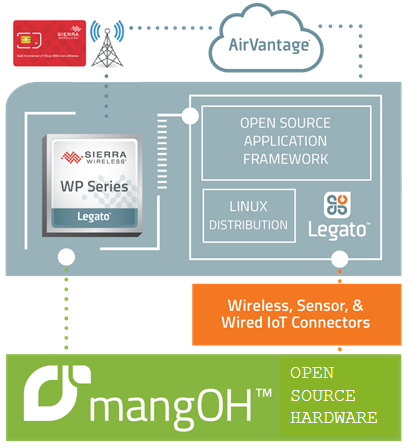
The platform includes the following components:
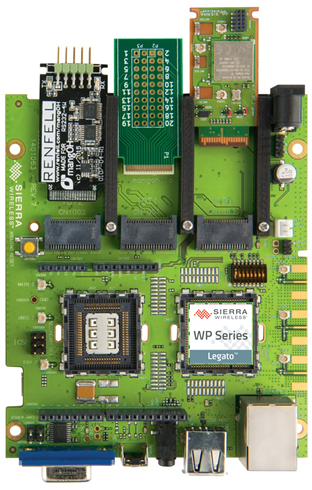
a. mangOH Green open hardware platform: mangOH Green is an open hardware reference design purpose built for cellular connectivity.
Smart WP module forms the core of the mangOH platform . It incorporates a telecom core that will provide 2G to 4G connectivity as well as a GNSS connection. It also has an application core with multiple interfaces like SPI,I2C,SDIO, HSIC, UART, USB. These interfaces allows developers to connect Wireless, Wired and sensor technologies. The present gen WP application core has a cortex A5 at 550MHz and 2Gb NAND and 1Gb RAM reserved for application development
mangOH allows you to use existing open hardware Arduino compatible shields. There is an Arduino compatible connector that allows any Arduino shields to be plugged on top of the mangoh.There is an onboard ATMega32u4 chipset directly talking to the WP module.We have a prebuilt legato bridge application allowing seamless connection between the Arduino shield and WP module. We have a two way data exchange between the Arduino shield and anyother application connected to the mangoh. We also provide a couple of additional APIs that allow you to push the data to the cloud. For the Hackathon, the Arduino Legato app (called Arduino Bridge) talks to the ATmega chipset and takes care of the bringing data from arduino sensors into the WP module
b.Legato Open Source Embedded Linux Framework: An open source Linux-based embedded platform designed to simplify connected IoT application development. Using Legato Framework developers with limited hardware, wireless, embedded or cloud expertise can build applications easily.
There are essentially 3 parts to Legato.
i. The first part is a Linux Distribution. Specifically, an it’s an embedded Linux distribution tailored to run on Sierra Wireless’s Linux-capable modules to start with (since Sierra has funded the whole project so far), with select security features enabled. Legato Linux is based on the Linux Foundation’s Yocto Project.
ii. The second part is the Legato Application Framework. This builds on top of standard POSIX and Linux APIs, complementing them. It includes Connectivity APIs and tools to make using cellular easy. It provides helpful tools for building and deploying embedded applications into the field. Includes support for multiple programming languages. And it also provides application sandboxing. That is all applications are isolated from each other to help prevent any problems in one application taking down another.
The framework update process also enables automatic rollback so that a bad software update will not brick your device.
iii. The third part is the development environment.
We start with command-line tools that help you:
- build your apps.
- configure your devices.
- install, remove, start, and stop apps on your devices.
- debug your running code.
We then add an Eclipse-based IDE, which supports most of the features offered by the command-line tools, and adds graphical tools for
- discovering target devices on your network.
- managing and editing files directly on your device via sftp.
- doing symbolic debugging using a graphical frontend to gdb.
- editing source code, with syntax highlighting and context-sensitive help.
c. Air Vantage cloud platform: AirVantage lets you capture and exploit data from any device deployed in the field, opening many new possibilities for your business processes, service applications, and revenue streams.
d. Sierra Wireless Smart SIM: The Sierra Wireless Smart SIM is specifically designed for mission critical mobile and fixed IoT use cases.
mangOH Green open hardware platform
More information on mangOH/Legato/AV can be found at:
c. How to use API with AirVantage.docx
Connectivity for the hackathon is provided by the following :
b. WiFi /BT IoT Expander card for Client or AP mode and to attach to BLE sensors
c. Location sensing is provided by an on board GPS.
d. Sierra Wireless Smart SIM
APIs for Hackathon
The APIs we will provide for building various IoT use cases include (but not limited to):
Legato API
i. Communication Manger/ Modem services (http://legato.io/legato-docs/latest/legatoServicesModem.html)
ii. Location Sensing (http://legato.io/legato-docs/latest/legatoServicesPositioning.html)
iii. WiFi: (http://legato.io/legato-docs/latest/legatoServicesWiFi.html)
iv. Data Router (https://github.com/mangOH/DataRouter/blob/master/dataRouter.api)
v. MQTT ( https://github.com/mangOH/MqttClient/blob/master/mqtt.api)
vi. Misc API found at legato.io
AirVantage API:
API to connect AirVantage to enterprise software (https://doc.airvantage.net/av/howto/gettingstarted/)
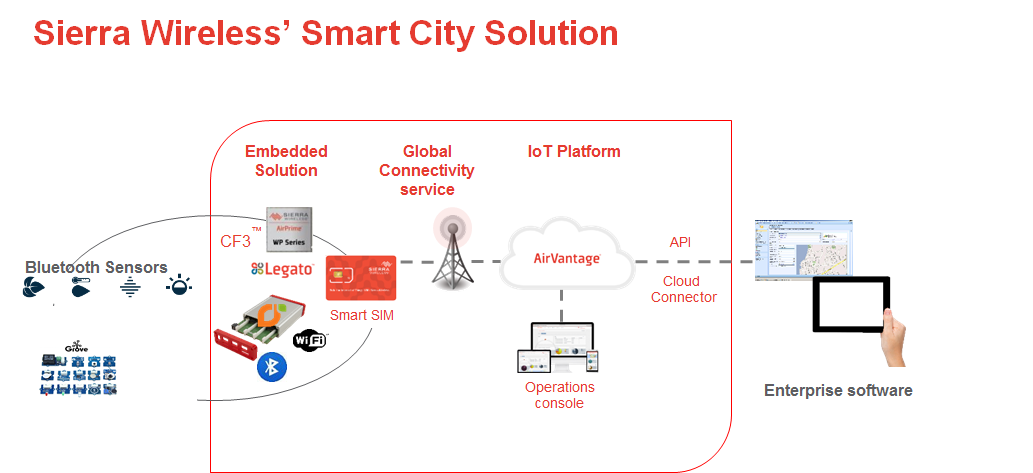
Hackathon Architecture
The IoT application will take input from various Bluetooth or Grove Studio sensors and provide actuator functions as needed . Bluetooth data collection is done by on board Bluetooth IoT expander card.
The sensors kit for the hackathon includes the following sensors:
a. Grove Studio sensors based : Temperature, Humidity, Dust, Oxygen, Noise, Light, Sound . Tutorial : 4119370_mangOH Green Tutorial - Arduino to AirVantage_r1.pdf
b. Bluetooth based: digital microphone, magnetic sensor, humidity, pressure, accelerometer, gyroscope, magnetometer, object temperature, and ambient temperature
http://www.ti.com/lit/wp/swry023/swry023.pdf.
The platform architecture for the hackathon will involve the following applications :
- Arduino app: Gathering & publishing data provided by the Grove studio sensors
- BT app: Gathering & publishing data using the BLE based Sensor Tag sensors
- WiFi app : Used to provide connectivity either in client or AP mode
- Twitter app: To push data to twitter
- Data Router: Provides a way for the apps to publish and subscribe to data as well as pushes it to the AirVantage cloud using MQTT or LWM2M
- MQTT: Provides mechanism to push data to the cloud
- Smart City app: Subscribes to sensor data from BT and Arduino app. Publishes set of chosen data to Cloud
Using the Hackathon Platform
Sierra will provide 16 completely assembled kits with the following:
1 .16 mangOH Open Hardware platforms
2. 16 Bluetooth/WiFi IoT Expander cards
3. 16 TI Sensor Tag 2.0 will be provide
4. 10 Arduino Sensor Grove Shields
Each individual mangOH platform will be preassembled for you:
a. 10 units will have all the Arduino sensors plugged in. The Arduino app will automatically start. Tutorial 4119370_mangOH Green Tutorial - Arduino to AirVantage_r1.pdf
b. One Ti Sensor Tag Bluetooth sensor will be in every box. Each unit will be automatically pre-associated to one sensor tag.
In case you run into issue, please the sensor tag into scan mode by pressing the power button.
Then to connect mangOH to sensor tag run the following commands on console:
hcitool lescan ( this will show you MAC address of sensor tag)
config set bleSensorInterface:/sensorMac < MAC address>
config get bleSensorInterface:/sensorMac (confiirms the attachment)
c. Turing on the WiFi : follow the tutorial 4119378_mangOH Green Tutorial - Wi-Fi_r1 - Draft C.PDF
d. Connecting to BlueMix: Step below
TBC tomorrow
For direct response to questions, please register on the forum at mangoh.io ( http://forum.mangoh.io/)